The patent, filed with the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office and first spotted by Patently Apple, is titled "Laptop computing device with discrete haptic regions" and explains how a MacBook could provide significantly expanded haptic feedback across multiple areas.
Since the 2015 MacBook, Apple has included the Force Touch trackpad on all of its new laptops, such as the MacBook Pro and MacBook Air. Beyond the ability to detect how much pressure is placed on the trackpad, the Force Touch trackpad also delivers haptic feedback.
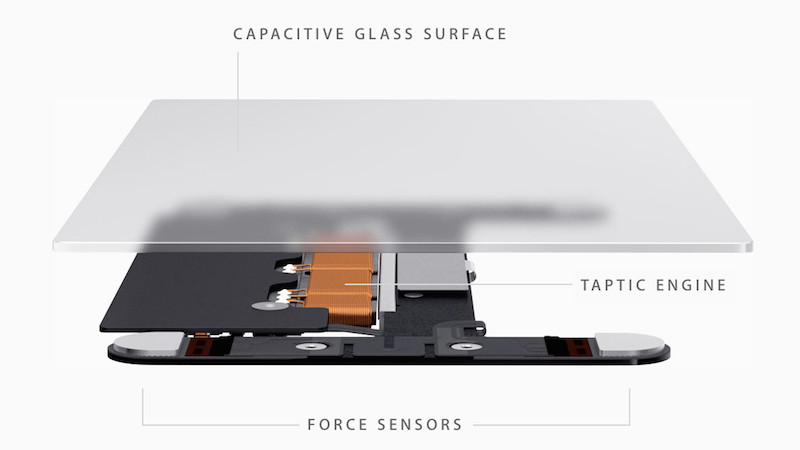
 The Taptic Engine currently used in the MacBook Pro and MacBook Air to deliver haptic feedback.
The Taptic Engine currently used in the MacBook Pro and MacBook Air to deliver haptic feedback.On MacBooks, haptic feedback is used to give the impression of a physical click, when the trackpad is actually static. In addition, it can offer useful contextual information in conjunction with on-screen content. For example, when moving a shape in a document or spreadsheet, haptic feedback is used to allow users to feel when it is in alignment with a margin or another object.
While haptics have thus far been reserved for the trackpad only on MacBooks, Apple is now actively researching how it can expand haptic feedback to more areas of the device.
Beyond simply making the technology more widespread on devices, Apple suggests that the utility of haptic feedback can be advanced by providing it in different areas to indicate a wider range of information. For example, haptic feedback could be distinctively provided on the left, middle, and right of a MacBook, and the feedback is said to be "imperceptible outside that region." Apple calls this system "spatially localized haptics."
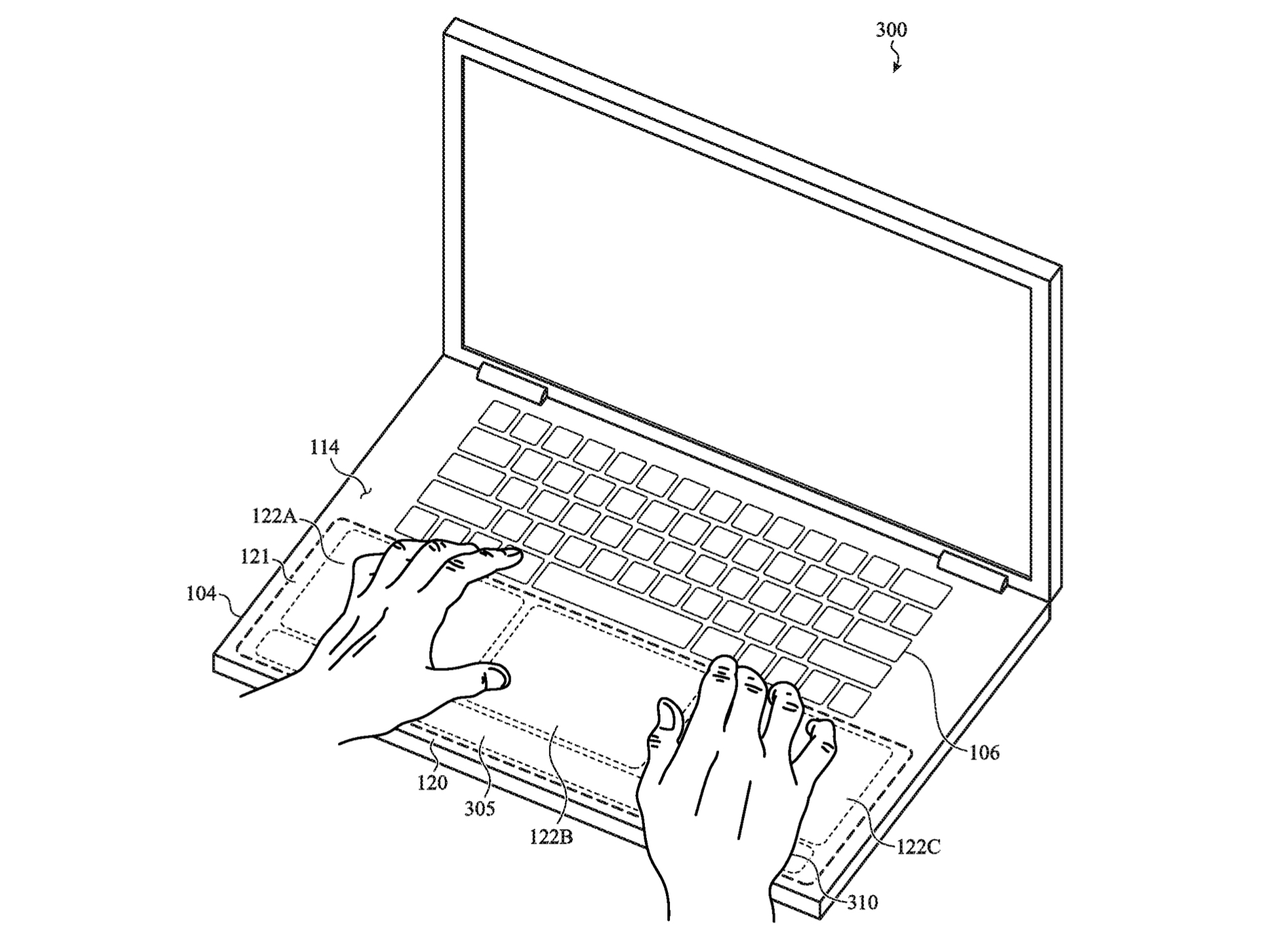
Some spatially localized haptics may overlap, but each has its own individual haptic actuator. Apple suggests that these areas may also be capable of accepting touch input to trigger haptic feedback. Interestingly, the patent notes that "force sensors" may be used to detect pressure input, presumably like the current implementation under the Force Touch Trackpad.
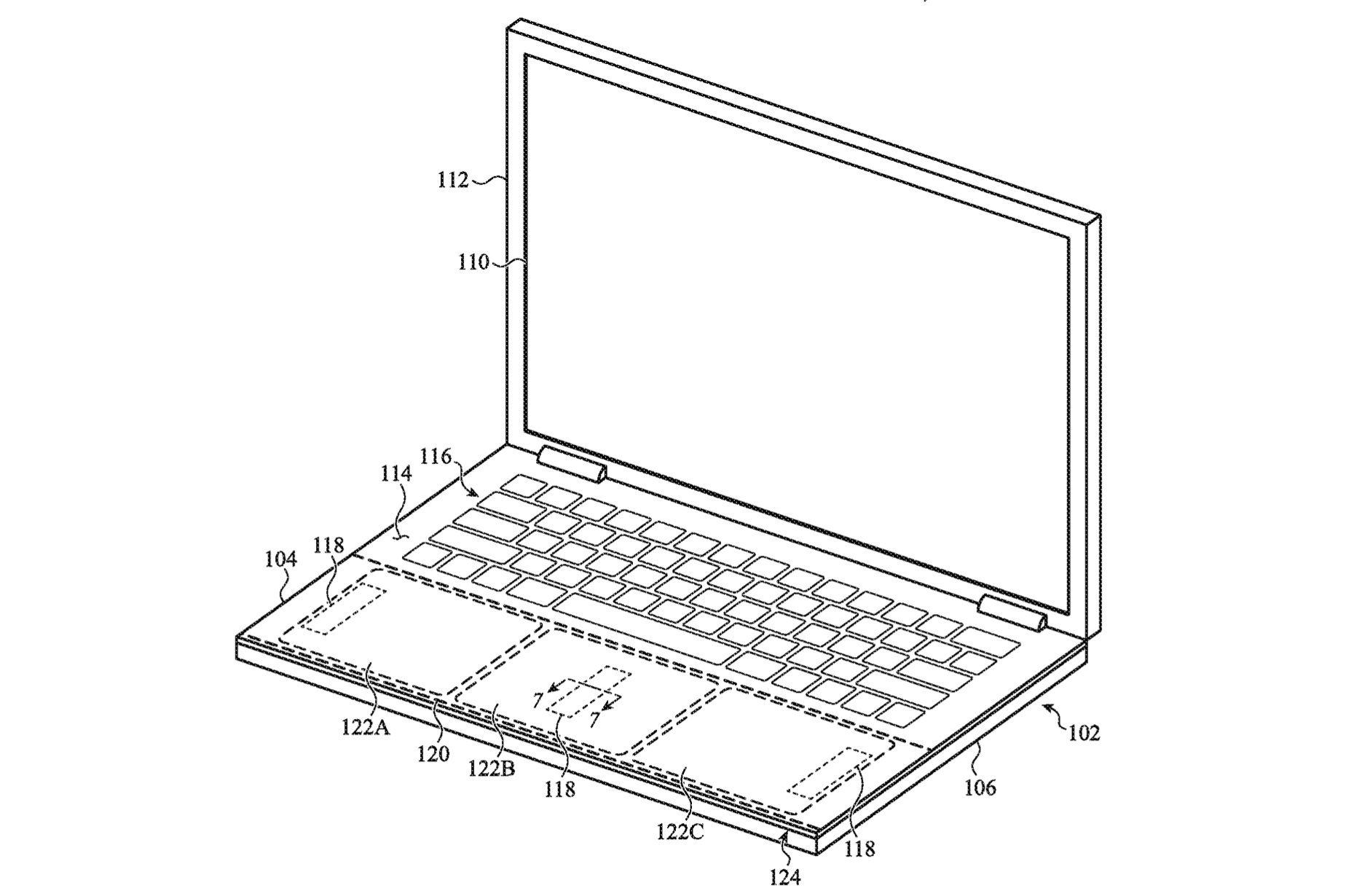
The system involves haptics that are so widespread that "an input area may encompass part of an electronic device's housing and be large enough that a user may touch multiple portions of the input area simultaneously."
Apple's spatially localized haptics are also said to be much more distinctive than normal haptic feedback, allowing users to clearly "distinguish between haptic outputs" in different areas.
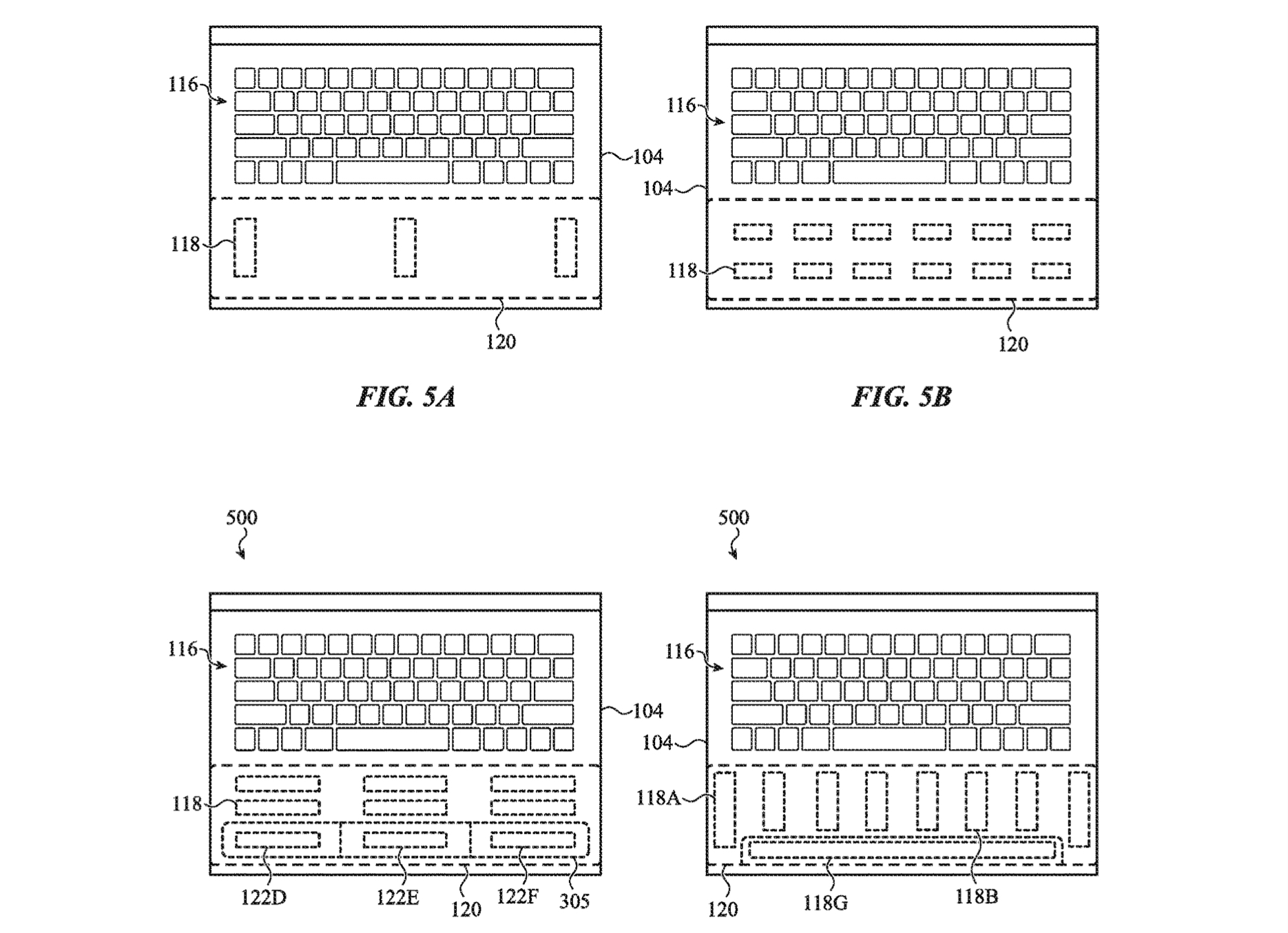
In terms of practical uses, the patent suggests that this system of spatially localized haptics could be used in response to the force of a user typing on a keyboard, offering an additional confirmation that an actuation force was registered. Alternately, the localized haptics may provide distinctive tactile outputs from either side of the palm rest, such as for a notification.
In much the same way that Apple uses different alert sounds on macOS to indicate different notifications, spatially localized haptics may offer a variety of tactile feedback for notifications. In some instances, "multiple haptic outputs may be provided simultaneously" to produce a different sensation and "alert a user to multiple notifications."
While patent filings cannot be taken as firm evidence of what Apple is intending to implement in its future products, they can offer an insightful look at the areas in which the company is directing its research and development. Unlike some patent filings which outline outlandish and abstract technologies that are very unlikely to come to market any time soon, this patent seems well within the realms of possibility, given that the technology already exists in millions of MacBook devices.
Tag: patent
This article, "Apple Exploring Wider Use of Haptic Feedback on MacBooks" first appeared on MacRumors.com
Discuss this article in our forums
via MacRumors: Mac News and Rumors - All Stories https://ift.tt/30y8bZX
No comments:
Post a Comment